Our bodies rely on a vast network of highways—our blood vessels—to transport blood throughout. This intricate system keeps us alive, but when it faces “traffic jams” or blockages, it can lead to serious health problems. According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, often due to blocked blood vessels. So, why do these vital highways get blocked, and what can we do about it?
How Blood Vessels Get Blocked
In our youth, blood vessels are smooth, elastic, and efficient. However, as we age and indulge in unhealthy lifestyles, our blood vessels begin to suffer:
- Wear and Tear:
- Over time, blood vessel walls can accumulate lipid streaks, much like rust in a pipe. Poor habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, a high-fat diet, and chronic stress can increase blood pressure, causing further damage to the vessel walls.

-
Formation of Plaque:
- Unhealthy lifestyles lead to the buildup of fatty deposits, or plaques, in the arteries. These plaques, made up of cholesterol crystals, cell debris, and calcium, narrow the arteries and obstruct blood flow.
-
Development of Blood Clots:
- When plaques rupture, the body responds by forming blood clots to heal the damage. These clots can further block the artery, leading to severe complications like heart attacks and strokes.
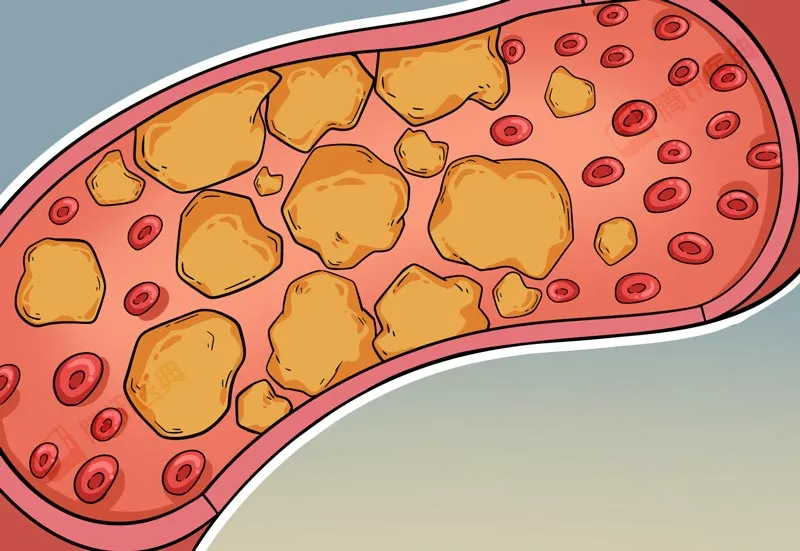
Consequences of Blocked Blood Vessels
The impact of blocked blood vessels varies depending on their location:
- Brain: Can cause strokes, leading to paralysis or even death.
- Heart: Can result in heart attacks, presenting symptoms like chest pain, palpitations, nausea, fatigue, sweating, dizziness, and difficulty breathing.
- Limbs: Can lead to numbness, coldness, pain, muscle cramps, and spasms.
- Kidneys: Can cause hypertension and kidney failure.
Bad Habits That Harm Blood Vessels
To protect your blood vessels, it’s crucial to avoid the following harmful habits:
- High-Fat, High-Salt, High-Sugar Diets:
- High Fat: Excessive fats from meats, fried foods, and processed snacks can clog arteries and increase blood viscosity, leading to clots.
- High Salt: High salt intake raises blood pressure, damaging blood vessels.
- High Sugar: Excess sugar hardens blood vessels, increasing the risk of blockages.
Improvement Tips:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit salt intake to less than 5 grams per day, and cooking oil to 25-30 grams per day.
- Keep added sugars below 50 grams per day, ideally under 25 grams.
- Prolonged Sitting and Lack of Exercise:
- Sedentary lifestyles can acutely damage blood vessel function, especially in the lower limbs, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes.
Improvement Tips:
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise weekly, such as dancing, cycling, jogging, or swimming.
- Incorporate physical activities into your daily routine, like walking, housework, and standing while working.
- Smoking:
- Nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco damage blood vessels and reduce oxygen delivery, accelerating aging and increasing disease risk.
Improvement Tips:
- Quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke. Consider support programs to aid in quitting.
- Frequent Late Nights:
- Lack of sleep and irregular sleep patterns increase stress hormones, causing blood vessel constriction and slower blood flow.
Improvement Tips:
- Prioritize regular sleep patterns, aiming for early nights and consistent wake times.
Myths About Blood Vessel Health
-
Eating Black Fungus Clears Blood Vessels:
- While black fungus contains beneficial dietary fibers and polysaccharides, its ability to clear blood vessels is exaggerated. Research on these effects uses extracts, not the whole food.
-
Regular IV Drips Clear Blood Vessels:
- No scientific evidence supports IV drips for clearing blood vessels or preventing diseases. Unnecessary IV treatments can harm the liver, kidneys, and heart.
-
Drinking Alcohol or Vinegar to Clear Blood Vessels:
- Alcohol is a cardiovascular risk factor, and vinegar does not soften blood vessels. Both can do more harm than good.
Conclusion
Protecting your blood vessels is essential for overall health. By avoiding high-fat, high-salt, and high-sugar diets, staying active, quitting smoking, and maintaining regular sleep patterns, you can keep your blood vessels clear and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Stay informed and take proactive steps to maintain your vascular health.

